

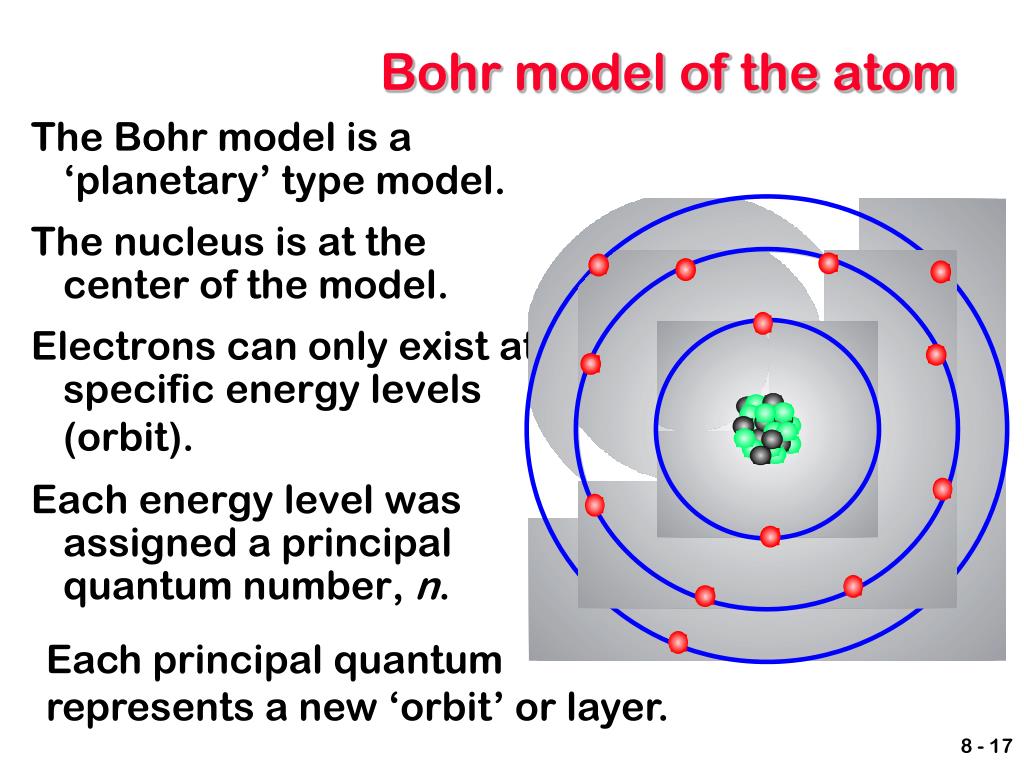
The various energy levels or orbits are represented in two ways: 1, 2, 3, 4… and K, L, M, N….When an electron loses energy, however, it shifts from a higher to a lower energy level. In an atom, electrons get the requisite energy to go from a lower to a higher energy level. When electrons jump from one energy level to another, they change their energy.Quantum numbers can have a wide range of values, ranging from the lowest energy level (nucleus side n=1) to the greatest energy level. Integers such as n=1 or n=2 or n=3 and so on are used to represent the various energy levels.As long as the electrons in the fixed orbital shells continue to rotate around the nucleus, they will not emit energy. Each round orbit has a predetermined amount of energy, and these circular orbits are referred to as orbital shells.Orbits, shells, and energy levels are the set circular paths electrons take around the nucleus.The postulates of Bohr’s atomic model are: Where l is the angular momentum, n is the Principle Quantum number, h is Planck’s constant.Īlso, The energy and radii of electron orbits in atoms are quantized, according to Bohr, with energy for transitions between orbits given by ∆E = hf = Ei − Ef, where ∆E is the difference in energy between the beginning and final orbits and hf is the energy of an absorbed or emitted photon.īohr Atomic Model- Postulates and Limitations Bohr Atomic Model- Postulates The energy lost by the electron during the sudden transition is identical to the energy of the emitted light quantum.īelow is the Bohr atomic Model of a Nitrogen atom.

He argued that light only emitted from hydrogen atoms when an electron moved from an outer orbit to one closer to the nucleus.
BOHR MODEL OF ATOM SERIES
Bohr was able to explain the series of discrete wavelengths in the hydrogen emission spectrum by restricting the orbiting electrons to a series of circular orbits with discrete radii. The German-born physicists James Franck and Gustav Hertz obtained direct experimental evidence for the existence of such discrete states in 1914.īohr changed his mind about the planetary electrons’ mobility to align the model with the regular patterns (spectral series) of light emitted by real hydrogen atoms. Only when electrons abruptly leap between permissible, or stationary, states do atoms absorb or release radiation. The properties of atomic electrons are described by the Bohr model and all of its successors in terms of a set of permissible (possible) values. It represented a significant break from earlier, classical representations. The Bohr Atomic model of the atom was the first to incorporate quantum theory and was the forerunner of entirely quantum-mechanical models. The Bohr Atomic model is a description of the structure of atoms, particularly hydrogen, proposed by Danish physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. Bohr Atomic Model- Postulates and Limitations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
